Every year, thousands of American healthcare facilities report safety incidents that highlight the importance of meticulous diagnostic procedures. Even one error can jeopardize patient outcomes and trust. With each step from verifying patient identification to reporting results, medical teams must apply unwavering accuracy. This guide walks through essential best practices for American healthcare professionals aiming to strengthen patient safety and uphold the highest standards of diagnostic care.
Table of Contents
- 1. Confirm Patient Identification And Test Orders
- 2. Review Patient Medical History And Symptoms
- 3. Choose The Appropriate Diagnostic Test
- 4. Prepare Proper Sample Collection Procedures
- 5. Ensure Accurate Labeling And Documentation
- 6. Follow Timely Transport And Processing Protocols
- 7. Review And Communicate Test Results Clearly
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Verify Patient Identity Thoroughly | Use at least two unique identifiers to confirm patient identity before diagnostic testing to prevent errors. |
| 2. Gather Comprehensive Medical History | Collect detailed health information to provide context for accurate diagnosis and testing decisions. |
| 3. Select Appropriate Diagnostic Tests | Match tests to patient symptoms and medical history for meaningful results and effective care. |
| 4. Implement Rigorous Sample Collection Procedures | Follow strict protocols to ensure sample integrity and reliability in diagnostic testing. |
| 5. Communicate Results Clearly | Translate complex medical data into understandable language to empower informed patient decisions. |
1. Confirm Patient Identification and Test Orders
Accurate patient identification represents the critical first step in any diagnostic testing procedure. Patient misidentification can lead to serious medical errors and compromised healthcare outcomes, making rigorous verification an absolute necessity.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services mandates strict protocols for confirming patient identity and test orders. Healthcare professionals must use at least two unique patient identifiers before initiating any diagnostic testing. These identifiers typically include the patient’s full name, date of birth, medical record number, or other specific personal information.
To ensure precise identification, medical staff should systematically cross reference patient information across multiple documents. This might involve comparing the patient’s identification bracelet, photo identification, medical records, and verbal confirmation. Electronic health record systems can provide additional verification layers by flagging potential discrepancies.
When receiving test orders, medical professionals must verify the order’s authenticity and completeness. This includes confirming the ordering physician’s credentials, ensuring all required diagnostic details are present, and validating the medical necessity of the requested tests.
Careful attention to patient identification protects both patients and healthcare providers from potential diagnostic errors. By implementing thorough verification processes, medical teams can significantly reduce the risk of sample mix ups, incorrect test results, and potential medical complications.
Pro tip: Create a standardized patient verification checklist that includes multiple identification cross reference steps and train all medical staff to follow these protocols consistently.
2. Review Patient Medical History and Symptoms
Comprehensive patient medical history review forms the foundation of accurate diagnostic testing. Understanding a patient’s complete health background provides critical context that can significantly impact test interpretation and results.
The CDC’s diagnostic excellence guidelines emphasize the importance of gathering a thorough medical narrative before conducting any diagnostic procedures. This involves collecting detailed information about existing medical conditions, prior diagnoses, current medications, allergies, family medical history, and recent symptoms.
Medical professionals should create a systematic approach to history collection that goes beyond surface level information. This means asking targeted questions that reveal potential interactions between current symptoms and past medical events. For instance, certain medications might interfere with test results, or previous conditions could predispose a patient to specific diagnostic challenges.
Effective medical history review requires active listening and careful documentation. Patients often provide subtle clues about their health through narrative details that might not immediately seem relevant. Skilled healthcare providers learn to connect seemingly unrelated symptoms or medical events to create a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s health landscape.
Symptom tracking becomes particularly crucial during this review process. Healthcare providers should document the onset, duration, intensity, and potential triggers of current symptoms. This granular approach helps create a more accurate diagnostic picture and supports more precise testing strategies.
Pro tip: Develop a standardized medical history questionnaire that covers comprehensive health domains and train staff to ask follow up questions that reveal deeper medical insights.
3. Choose the Appropriate Diagnostic Test
Selecting the right diagnostic test requires careful consideration of multiple clinical factors and patient specific needs. The testing process is far more nuanced than simply ordering a random set of medical examinations.
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services guidelines emphasize that diagnostic tests must be reasonable and necessary for the patient’s specific medical condition. This means healthcare providers must evaluate several critical elements when determining the most appropriate testing approach.
The selection process involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s presenting symptoms, medical history, current health status, and potential underlying conditions. Medical professionals must consider factors such as test sensitivity, specificity, potential risks, cost effectiveness, and the likelihood of obtaining clinically meaningful results.
Different diagnostic tests serve unique purposes and provide varying levels of insight. Blood tests can reveal metabolic issues and infection markers. Imaging studies like X rays or MRIs can visualize structural abnormalities. Genetic tests can uncover hereditary predispositions. The key is matching the most precise diagnostic tool to the specific clinical question being investigated.
Practical implementation requires a systematic approach. Healthcare providers should consult current medical literature, review established clinical guidelines, and consider the patient’s individual risk factors. Collaboration between primary care physicians, specialists, and laboratory professionals can help ensure the most appropriate testing strategy.
Pro tip: Create a decision matrix that cross references patient symptoms with recommended diagnostic tests to streamline the selection process and reduce potential diagnostic oversights.
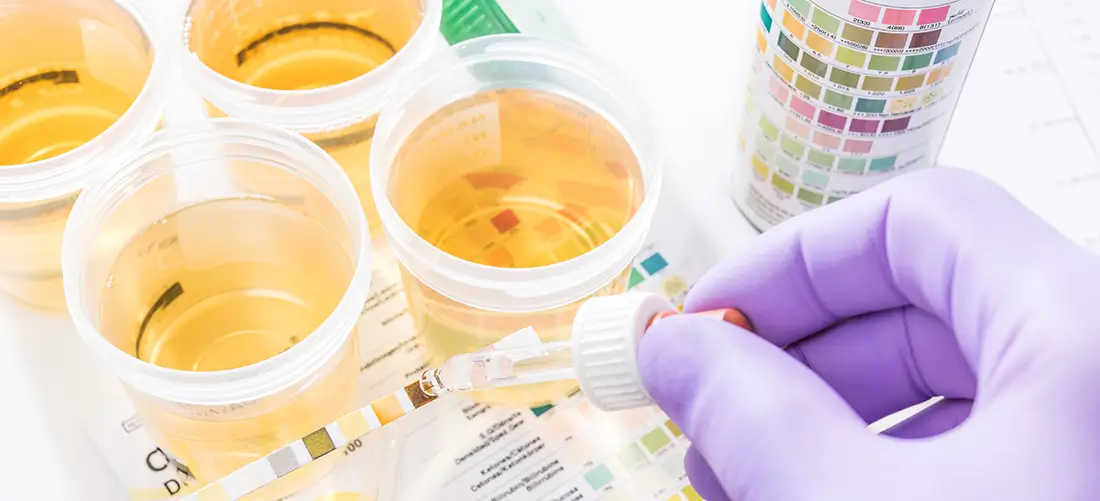
4. Prepare Proper Sample Collection Procedures
Proper sample collection represents a critical step in ensuring diagnostic accuracy and reliability. The integrity of medical test results depends entirely on how carefully and systematically samples are gathered and processed.
The CDC’s diagnostic testing guidelines emphasize the importance of establishing rigorous sample collection protocols that minimize potential contamination and error. These procedures require meticulous attention to detail and strict adherence to standardized medical practices.
Sample collection involves multiple key considerations beyond simply obtaining biological material. Healthcare professionals must ensure proper patient preparation, use appropriate collection tools, maintain precise environmental conditions, and follow strict handling protocols. Different types of samples blood, urine, tissue, or respiratory specimens require unique collection techniques that preserve their diagnostic potential.
Effective sample collection demands comprehensive staff training and consistent procedural standards. This includes understanding proper personal protective equipment usage, sterilization techniques, labeling protocols, and transportation requirements. Medical teams must create a systematic approach that reduces human error and maintains sample integrity from collection through laboratory analysis.
The preparation process also requires clear communication with patients. Explaining collection procedures, answering questions, and ensuring patient comfort can significantly improve sample quality and reduce patient anxiety. Some tests may require specific patient instructions such as fasting or avoiding certain medications before sample collection.
Pro tip: Develop a standardized sample collection checklist that includes verification steps for patient identity, sample type, collection method, and immediate preservation requirements.
5. Ensure Accurate Labeling and Documentation
Accurate specimen labeling and documentation serve as the critical backbone of reliable diagnostic testing. A single error in identification can potentially compromise patient safety and lead to significant medical complications.
The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute establishes rigorous standards for specimen management that require meticulous attention to detail. Healthcare professionals must implement comprehensive labeling protocols that create an unambiguous link between the patient and their diagnostic samples.
Effective documentation involves more than simply writing a patient name on a test tube. It requires capturing multiple precise identifiers including full name, medical record number, date and time of collection, and the healthcare professional responsible for obtaining the sample. Electronic tracking systems can provide additional layers of verification and reduce human error.
Each sample must be labeled immediately after collection to prevent potential mix ups or misidentification. This means using waterproof labels, writing clearly and legibly, and including all necessary identifying information. Standardized color coding systems can provide additional visual verification for different types of specimens.
Healthcare teams should develop systematic training programs that emphasize the critical nature of proper documentation. This includes creating clear guidelines, conducting regular audits, and implementing fail safe procedures that catch potential documentation errors before they can impact patient care.
Pro tip: Implement a two person verification process for specimen labeling where two independent healthcare professionals cross check each sample’s identification information before processing.
6. Follow Timely Transport and Processing Protocols
Timely transport and processing of medical specimens represent a crucial link in maintaining diagnostic accuracy. Every minute matters when preserving the biological integrity of test samples.
The CDC’s diagnostic testing guidelines underscore the critical nature of swift specimen management. Different biological samples have unique stability windows that require precise handling to prevent degradation or contamination.
Transport protocols demand specialized environmental controls. Blood samples might require refrigeration, while molecular testing specimens could need immediate freezing. Temperature sensitive tests have narrow processing windows that medical professionals must understand and respect. Specialized transport containers with precise thermal regulation help maintain sample quality during transit.
Healthcare teams must develop comprehensive tracking systems that monitor specimen movement from collection point to laboratory. Digital logging technologies can provide real time updates about sample location and environmental conditions. This approach reduces potential errors and provides accountability throughout the testing process.
Professional laboratories implement strict time sensitive protocols that outline maximum allowable transit times for different specimen types. These guidelines consider factors like sample volume, collection method, and specific diagnostic requirements. Understanding these nuanced protocols helps prevent test result inaccuracies.
Pro tip: Create a color coded tracking system that visually indicates specimen type, collection time, and required processing window to streamline laboratory workflow and minimize potential handling errors.
7. Review and Communicate Test Results Clearly
Communicating diagnostic test results represents the critical final step in the medical testing process. Clear, compassionate communication transforms raw data into meaningful healthcare guidance.
The CDC’s patient safety guidelines emphasize the importance of comprehensive result interpretation that goes beyond simple numerical reporting. Healthcare professionals must translate complex medical information into understandable language that empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health.
Effective result communication requires a multilayered approach. This means providing context around test numbers explaining what they mean, potential implications, and recommended next steps. Medical professionals should anticipate patient questions and proactively address potential concerns during result discussions.
Technical language can often intimidate patients and create unnecessary anxiety. Successful communication involves breaking down complex medical terminology into simple conversational explanations. Using analogies visual aids and patient friendly descriptions can help demystify diagnostic information and reduce patient stress.
Written documentation should complement verbal explanations. Providing patients with clear written summaries that include test results, professional interpretations, and follow up recommendations ensures they have a reliable reference for understanding their health status.
Pro tip: Develop a standardized result communication template that includes plain language explanations, visual representations of key data points, and clear guidance on potential next steps for patient care.
This table summarizes the key steps and processes for effective diagnostic testing, highlighting best practices and expected outcomes.
| Main Step | Key Points & Actions | Benefits/Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Confirm Patient Identification | Use two unique identifiers like full name and DOB; cross-reference documents; verify test order details. | Reduces risk of misidentification and medical errors. |
| Review Patient Medical History | Collect comprehensive medical history; ask targeted questions; track symptoms. | Provides critical context for accurate test interpretation. |
| Choose the Appropriate Diagnostic Test | Evaluate symptoms, medical history, test sensitivity and risks; consult guidelines and collaborate with specialists. | Ensures clinically meaningful and cost-effective testing. |
| Prepare Proper Sample Collection | Follow standardized protocols; use appropriate tools; ensure patient preparation and communication. | Maintains sample integrity and diagnostic reliability. |
| Ensure Accurate Labeling & Documentation | Label samples immediately with comprehensive identifiers; implement electronic tracking. | Prevents sample mix ups and enhances patient safety. |
| Follow Timely Transport & Processing | Adhere to environmental controls and tight timeframes; utilize tracking systems. | Preserves biological integrity and accurate test results. |
| Review & Communicate Test Results | Provide results in understandable language; anticipate questions; offer written documentation. | Empowers patients with clear health guidance and next steps. |
Strengthen Your Diagnostic Testing with Centra Diagnostics Today
Accurate patient identification, proper sample handling, and clear result communication are critical to avoid costly diagnostic errors and ensure better healthcare outcomes. If you want to overcome challenges like sample mix ups or delayed test results, partnering with a trusted diagnostics lab that prioritizes precision and speed is essential. Centra Diagnostics in Los Angeles offers advanced molecular testing, toxicology, blood work, and COVID-19 testing solutions that align perfectly with the checklist steps outlined in this article.

Empower your clinical decisions by choosing a laboratory that follows rigorous identification protocols, uses cutting-edge technology, and guarantees fast turnaround times. Explore how our client-centered approach makes navigating complex diagnostic requirements seamless. Visit Centra Diagnostics now and experience diagnostic services designed to support healthcare providers and patients alike. Take the first step toward reliable, effective testing solutions and improve patient care today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key steps involved in an effective diagnostic testing checklist?
The key steps include confirming patient identification, reviewing patient medical history and symptoms, choosing the appropriate diagnostic test, preparing proper sample collection procedures, ensuring accurate labeling and documentation, following timely transport and processing protocols, and clearly communicating test results. To implement this, create a checklist that incorporates these essential steps to streamline your diagnostic testing process.
How can I ensure accurate patient identification before diagnostic testing?
To ensure accurate patient identification, use at least two unique identifiers, such as the patient’s full name and date of birth. Systematically cross-reference this information across multiple sources, including identification bracelets and medical records, to minimize the risk of misidentification.
What should I include in a standardized medical history questionnaire?
Include comprehensive questions covering existing medical conditions, prior diagnoses, current medications, allergies, family medical history, and recent symptoms. Develop targeted questions that probe deeper into the patient’s narratives to reveal crucial health insights that are relevant to their current condition.
How can I improve the accuracy of specimen labeling and documentation?
Enhance accuracy by capturing multiple identifiers, including full name, medical record number, and date and time of sample collection on the labels. Train your staff to label each sample immediately after collection to prevent mix-ups and implement a two-person verification system for additional accuracy.
What are best practices for transporting and processing specimens in a timely manner?
Adopt specialized transport protocols that consider the stability requirements of different sample types, such as refrigeration for blood samples. Create a color-coded tracking system to monitor sample movement and ensure adherence to maximum allowable transit times to maintain specimen integrity.
How can I effectively communicate diagnostic test results to patients?
Communicate results clearly by using plain language to explain the significance of the test numbers and their implications for patient health. Provide written documentation that summarizes test results alongside verbal explanations to empower patients in understanding their health status and next steps.